
The Cosumnes River Preserve in the Central Valley of California. Photo: Photo: © Karen Gregg Elliott/TNC
How much groundwater do ecosystems need to survive?

The Cosumnes River Preserve in the Central Valley of California. Photo: Photo: © Karen Gregg Elliott/TNC
When California enacted the Sustainable Groundwater Management Act (SGMA) in 2014 it was the last state to pass comprehensive groundwater legislation, but was the first and only state to specifically require that the needs of nature be included in the management of groundwater. In addition to balancing the needs of people and nature, groundwater sustainability agencies (GSAs) must identify and consider the groundwater needs of ecosystems.
But how? And how much groundwater do ecosystems need? What thresholds must be maintained for plants and animals to survive?
The Cosumnes River Preserve in California’s Central Valley is a complex of properties purchased by the Conservancy and partners beginning in 1984. The early goal of the Preserve was to expand riparian forests by protecting and restoring floodplain ecosystems. For the past two decades, Conservancy scientists have investigated the linkages between riparian forest health, groundwater and surface water.
Through the years, the Conservancy and partners launched groundwater and vegetation monitoring programs to identify optimal management for conditions to maintain a healthy ecosystem. Through years of observation, they hypothesized that groundwater was playing a larger role than previously thought. Today, we are tapping these long-term studies to see how groundwater conditions are linked to the health of the ecosystem above ground.
In 2017, in partnership with Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Conservancy scientists dug a little deeper at the Cosumnes by employing a geophysical approach to take “x-rays” of the ground to detect groundwater. The images revealed that the healthiest forests had the greatest access to groundwater–supporting their hypothesis.
This on-the-ground research in the Cosumnes couples biological and hydrological datasets to determine the groundwater thresholds and baseline conditions required to sustain ecosystem health. This is the type of information GSAs need to sufficiently and successfully include nature in their plans required under SGMA.
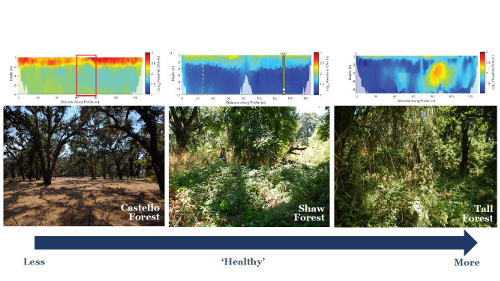
Geophysical approaches that help us “see” groundwater are helping to characterize groundwater conditions under forests. Warmer colors indicate dry sands and cooler colors indicate wet silts and clays.
Rohde, M.M., S. Matsumoto, J. Howard, S. Liu, L. Riege, E.J. Remson
California's Sustainable Groundwater Management Act (SGMA) of 2014 is landmark legislation that empowers local agencies, known as groundwater sustainability agencies, to sustainably manage…Melissa M. Rohde, Ray Froend, Jeanette Howard
Groundwater is a vital water supply worldwide for people and nature. However, species and ecosystems that depend on groundwater for some or all of their water needs, known as groundwater dependent…Kirk Klausmeyer, Jeanette Howard, Sandi Matsumoto, Sally Liu, Melissa Rohde
Groundwater is essential to the health and viability of plants, animals and ecosystems. Many tree species, like willows and cottonwoods, rely on groundwater to survive seasonal and annual dry spells.…The Nature Conservancy, RMC Consultants, Inc.
Groundwater is intimately connected to surface water, which has profound implications for sustainable water resource management. California has historically overlooked this important interaction and…The Nature Conservancy, RMC Consultants, Inc.
Groundwater is intimately connected to surface water, which has profound implications for sustainable water resource management. California has historically overlooked this important interaction and…